How to Run MongoDB Workloads with FerretDB on Tembo

FerretDB adds MongoDB compatibility to relational DBs like Postgres and SQLite.
Tembo is the Postgres developer platform for building every data service; it provides a fully extensible managed Postgres service. Through Tembo, developers can quickly spin up specialized data services using Stacks and pre-built PostgreSQL configurations and deploy them without complex builds, Docker installations, or additional data teams.
In this blog post, we'll show you how to run FerretDB on Tembo for your production workloads.
Prerequisites
- Tembo account (https://tembo.io/docs/tembo-cloud/getting_started)
mongoshpsql
FerretDB stack on Tembo
In Tembo, stacks are pre-built Postgres configurations optimized for enterprise use. So in just a few clicks, you have ready-to-use Postgres deployments for most of your data needs. This can be an advantage for adopting or managing a new database.
The FerretDB stack is available on Tembo as "Mongo Alternative on Postgres". The stack has been optimized for document store workloads, and you can still update some of the features or extend it with any of the numerous Postgres extensions on Tembo. And Tembo not only hosts your managed Postgres instance but also FerretDB in a container next to your database which helps in reducing latency while accessing FerretDB.
Learn more about Tembo stacks.
Create a FerretDB database on Tembo
Once you have an account on Tembo, go ahead to create an instance of FerretDB. Select the "Mongo Alternative on Postgres" Stack, as shown below.
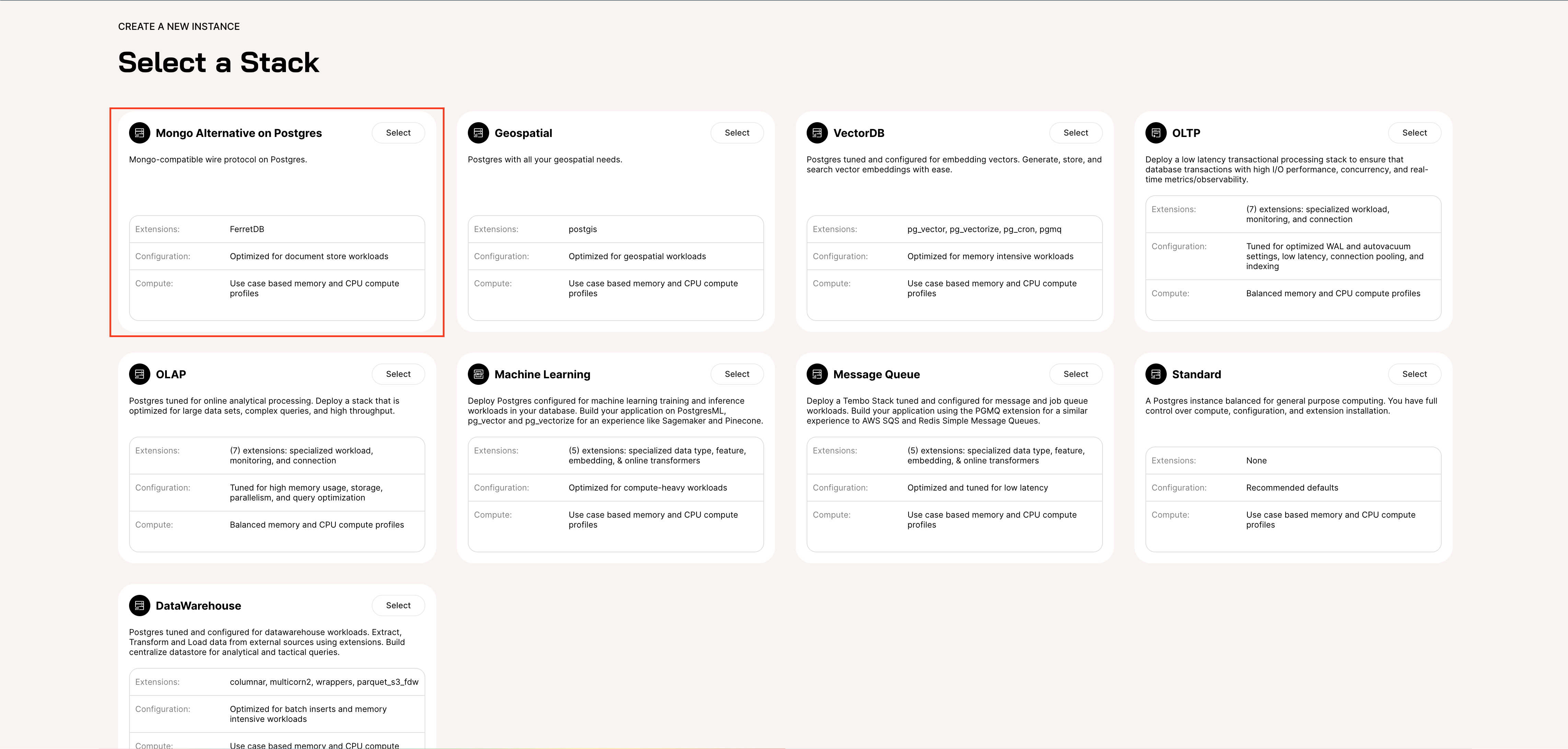
Next, configure your instance with the appropriate cloud provider, instance type, storage size, and region. Then click "Create". It might take a few minutes to provision the instance.
You can access these connection string, username, password, and host credentials by displaying the connection details for your instance.
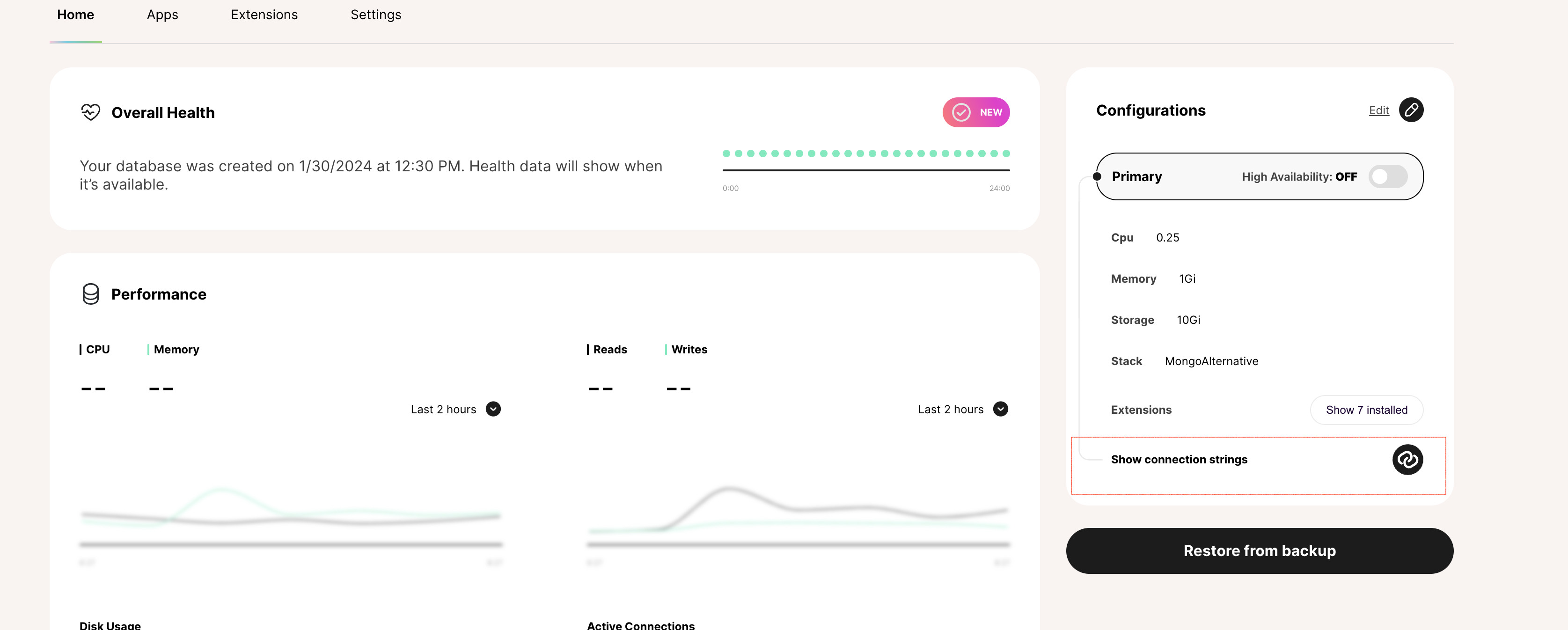
Your connection string for the FerretDB instance on Tembo follows the below format:
mongodb://<USERNAME>:<PASSWORD>@<HOST>:27017/ferretdb?authMechanism=PLAIN&tls=true&tlsCaFile=$(pwd)/ca.crt
You need to download the root SSL certificate from the connection detail dashboard.
The tlsCaFile=$(pwd)/ca.crt in the connection string specifies the SSL certificate file's location using the current directory ($(pwd)).
If you prefer a different directory, replace $(pwd)with the path to the certificate, liketlsCaFile=/your/certificate/path/ca.crt.
Import JSON record into FerretDB instance
From the directory of the SSL cert you downloaded, connect to the instance directly via mongosh.
Let's import a supply records containing into the ferretdb database using mongoimport.
This dataset provides a detailed look into a purchase record.
Here is the record for the imported JSON file
mongoimport --uri="<mongodb-connection-string>" --db ferretdb --collection supply --file /path/to/exportedFile.json
Be sure to update with the correct connection string.
Connect to FerretDB instance on Tembo via mongosh
Once the import is successful, let's connect to our instance via mongosh from the directory containing the SSL Certificate.
mongosh "<mongodb-connection-string>"
We will run some practical examples to showcase FerretDB on Tembo and how you can use it.
Example 1: Viewing a single supply purchase record
To understand the structure and type of data in the supply collection, let's check out a single "supply" purchase record. This example illustrates the kind of information captured in each transaction.
db.supply.findOne()
Result:
{
"_id": ObjectId("65c0d6d5cfba3092d3958fbf"),
"transaction_id": 10004,
"customer_name": "Jorge Lopez",
"customer_location": "Madrid, Spain",
"product_category": "Sports Equipment",
"transaction_time": ISODate("2023-07-10T10:00:00.000Z"),
"product_name": "Adidas Running Shoes",
"price": 75,
"quantity": 2,
"payment_method": "Bank Transfer"
}
Awesome! The record shows a purchase made by Jorge Lopez, who bought 2 pairs of Adidas Running Shoes for $75.
Example 2: Finding data for a specific period
To analyze our supply data over specific periods, we can query the collection record within the desired date ranges. This could be useful in understanding the impact of a particular promotional campaign.
db.supply.find({
transaction_time: {
$gte: ISODate('2023-07-01T00:00:00.000Z'),
$lte: ISODate('2023-07-03T23:59:59.000Z')
}
})
Result:
[
{
_id: ObjectId('65c0d6d5cfba3092d3958fdb'),
transaction_id: 10032,
customer_name: 'Emma Olsen',
customer_location: 'Bergen, Norway',
product_category: 'Electronics',
transaction_time: ISODate('2023-07-01T14:00:00.000Z'),
product_name: 'Amazon Echo',
price: 99,
quantity: 1,
payment_method: 'Bank Transfer'
},
{
_id: ObjectId('65c0d6d5cfba3092d3958fdc'),
transaction_id: 10033,
customer_name: 'Jens Petersen',
customer_location: 'Copenhagen, Denmark',
product_category: 'Fashion',
transaction_time: ISODate('2023-07-02T15:00:00.000Z'),
product_name: 'Fossil Watch',
price: 150,
quantity: 1,
payment_method: 'MobilePay'
},
{
_id: ObjectId('65c0d6d5cfba3092d3958fea'),
transaction_id: 10047,
customer_name: 'Sarah Johnson',
customer_location: 'Sydney, Australia',
product_category: 'Electronics',
transaction_time: ISODate('2023-07-03T13:00:00.000Z'),
product_name: 'Dell Laptop',
price: 1200,
quantity: 1,
payment_method: 'Credit Card'
},
{
_id: ObjectId('65c0d6d5cfba3092d3958feb'),
transaction_id: 10048,
customer_name: 'Mehmet Yilmaz',
customer_location: 'Istanbul, Turkey',
product_category: 'Fashion',
transaction_time: ISODate('2023-07-03T14:00:00.000Z'),
product_name: 'Handmade Bag',
price: 80,
quantity: 1,
payment_method: 'Debit Card'
}
]
This query filters the records to only include transactions that occurred between the 1st and 3rd of July 2023.
Example 3: Identifying the most bought item
Say you want insight into the most in-demand item. We can aggregate the data to sum the quantities sold by product name.
db.supply.aggregate([
{
$group: {
_id: '$product_name',
totalQuantity: { $sum: '$quantity' }
}
},
{ $sort: { totalQuantity: -1 } },
{ $limit: 1 }
])
Result:
[{ _id: 'The Alchemist', totalQuantity: 5 }]
This operation groups the records by product_name, sums up the quantities, and then sorts the results in descending order of quantity to highlight the most popular item.
These are just a few examples of how FerretDB can run MongoDB workloads for many use cases. You can go ahead to try other operations on FerretDB.
Get started with FerretDB on Tembo
Running FerretDB enables you to run MongoDB workloads on a high-performance, fully extensible managed Postgres service. Tembo also provides you with a host of resources and extensions without any complex builds or need to run Docker.
So if you want to migrate from MongoDB and you are looking to run MongoDB workloads on a managed Postgres service, you can get started with FerretDB on Tembo today.
If you have any questions or comments about FerretDB, contact us here.
